Spect Scan vs PET Scan: Understanding the Differences and Choosing the Right Test for You
Guide or Summary:Spect Scan: A Brief OverviewPET Scan: A Brief OverviewKey Differences Between Spect and PET Scans Imaging Principles and Techniques Radiotr……
Guide or Summary:
- Spect Scan: A Brief Overview
- PET Scan: A Brief Overview
- Key Differences Between Spect and PET Scans
- Imaging Principles and Techniques
- Radiotracer Use
- Diagnostic Applications
- Choosing the Right Test for You
In the realm of medical imaging, selecting the appropriate diagnostic tool is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Two such tools that have gained prominence in recent years are Spectral Computed Tomography (Spect) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Both imaging modalities offer unique insights into the body's internal workings, but how do they differ, and which one is better suited for your specific needs? This detailed comparison will shed light on the distinctions between Spect vs PET scans, helping you make an informed decision on which imaging test to undergo.
Spect Scan: A Brief Overview
Spect Scan, or Spectral Computed Tomography, is a diagnostic imaging technique that combines positron emission tomography (PET) with X-ray computed tomography (CT). This fusion allows for the acquisition of both anatomical and functional information simultaneously. Spect scans are particularly useful for assessing blood flow, oxygenation, and metabolic activity within tissues.
PET Scan: A Brief Overview
On the other hand, PET Scan, or Positron Emission Tomography, is a nuclear imaging technique that involves the injection of a small amount of a radioactive substance into the patient's body. This substance, known as a radiotracer, is designed to be absorbed by specific tissues or organs and emits positrons when decaying. By detecting these positrons, PET scans provide detailed images of metabolic processes occurring within the body.
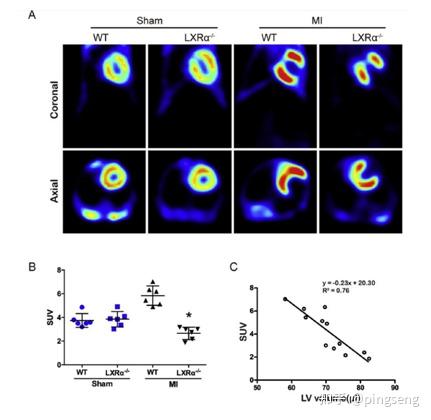
Key Differences Between Spect and PET Scans
While both Spect and PET scans offer valuable insights into the body's internal functions, there are several key differences to consider:
1. Imaging Principles and Techniques
Spect scans combine PET and CT technologies, offering a blend of anatomical and functional information. This dual-modality approach allows for a more comprehensive assessment of the body's internal structures and their metabolic functions.
In contrast, PET scans primarily focus on the metabolic activity of tissues and organs. By detecting the decay of radiotracers, PET scans provide detailed images of metabolic processes, making them particularly useful for diagnosing conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
2. Radiotracer Use
Spect scans use both positron-emitting and gamma-emitting radiotracers, allowing for the assessment of both metabolic and anatomical information. This dual-tracer approach provides a more comprehensive view of the body's internal structures and their metabolic functions.
PET scans, on the other hand, primarily rely on positron-emitting radiotracers. These tracers are designed to be absorbed by specific tissues or organs and emit positrons when decaying. By detecting these positrons, PET scans provide detailed images of metabolic processes occurring within the body.
3. Diagnostic Applications
Spect scans are particularly useful for diagnosing conditions that require both anatomical and functional information. For example, they are commonly used for assessing blood flow, oxygenation, and metabolic activity in the heart, brain, and other organs.
PET scans, on the other hand, are highly effective for diagnosing a wide range of conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. They provide detailed images of metabolic processes, making them particularly useful for identifying abnormalities in tissue function.
Choosing the Right Test for You
Ultimately, the choice between a Spect scan and a PET scan depends on your specific medical needs and the condition being investigated. If you require both anatomical and functional information, a Spect scan may be the better option. Conversely, if you need detailed images of metabolic processes, a PET scan may be more appropriate.
In conclusion, both Spect and PET scans offer valuable insights into the body's internal workings, but they differ in their imaging principles, radiotracer use, and diagnostic applications. By understanding these differences, you can make an informed decision on which imaging test is best suited for your specific needs. Remember, it's always best to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate imaging test for your individual situation.